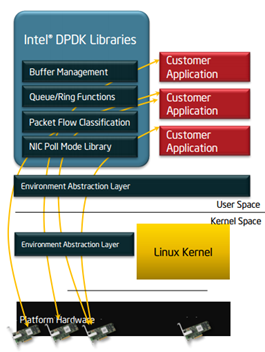
 Intel DPDK is a set of libraries and Ethernet drivers (native and virtualized) that run in Linux user space for fast packet processing on Intel Architecture.
Intel DPDK is a set of libraries and Ethernet drivers (native and virtualized) that run in Linux user space for fast packet processing on Intel Architecture.
Implements a run-to-completion or pipeline model.
No scheduler; all devices are accessed by polling.
Supports 32-bit/64-bit with/without NUMA.
Provides Environment Abstraction Layer (EAL) and Boot Code –platform-specific boot guidelines and initialization code to ease application porting effort.
BSD licensing model.Source downloadable from Intel and leading eco partners.
DPDK application runs as a user-land process.
DPDK I/O modules bypasses Linux kernel transport stack.
Core Libraries

Memory Manager Responsible for allocating pools of objects in memory. A pool is created in huge page memory space and uses a ring to store free objects.
Buffer Manager Reduces by a significant amount the time the operating system spends allocating and de-allocating buffers. The Intel DPDK pre-allocates fixed size buffers which are stored in memory pools.
Queue Manager Implements safe lockless queues, instead of using spinlocks, that allow different software components to process packets, while avoiding unnecessary wait times.
Flow Classification Provides an efficient mechanism which incorporates Intel Streaming SIMD Extensions to produce a hash based ontupleinformation so that packets may be placed into flows quickly for processing, thus greatly improving throughput.
Poll Mode Drivers (PMD) The Intel DPDK includes Poll Mode Drivers for 1GbE,10GbE and 40GbE Ethernet controllers which are designed to work without asynchronous, interrupt-based signaling mechanisms, which greatly speeds up the packet pipeline.
Kernel Version >= 2.6.33
glibc >= 2.7 (for features related to cpuset)
Kernel configuration needs the following to be enabled
-UIO Support
-HUGETLBFS
-PROC_PAGE_MONITOR
-HPET & HPET_MMAP (if HPET support is needed)
Core Components Architecture

Environment Abstraction Layer(EAL)
Hides environment specifics from the applications and DPDK libraries.
DPDK loading and launching
Provides support for multi-process and multi-thread execution types
Allocation of system memory.
CPU feature Identification
Interrupt handling
Core affinity/assignment procedures
Time reference
PCI bus access
Trace and debug functions

Queue/Ring Management
Lockless for single or multi-producer, single or multi-consumer enqueue/dequeue
Bulk enqueue and dequeue of specified count of objects if successful, otherwise fails.
Burst enqueue and dequeue of maximum available objects if specified count cannot be fulfilled.
Implements high & low watermarks for flow-control.
Effectively a fixed size FIFO implementation in SW.
Typically used for optimizing throughput.
E.g., decoupling stages of a pipeline, communication between cores etc.

- Fast due to use of single CAS instructions for multi-user case.
- Size of the queue is fixed and hence packets will be discarded at enqueue if the consumer is slower than the producer.
- Fixed memory for queue even when queue is empty.

Buffer Management (mem-pool)
- Allocates memory from EAL and creates pools with fixed element sizes.
- Number of elements and element size is user defined.
- Pools are based on Intel DPDK rings so are multi-producer and multi-consumer safe; no locking.
- Pools can also be used in multi-process environments.
- Typical usage is for packet buffers

For performance the following is supported.
- Cache alignment
- Per core buffer caches for each buffer pool.
- Support for bulk allocation/free .
- rte_malloc is supported, but should not be used in data Path because management of fragmented heap is costly and allocator is not optimized for parallel allocations.
Debugging support (debug-mode only)
- Cookies are added at the beginning and end of the blocks to check for overflow.
- APIs are available to get usage statistics
Check for double free is not supported.

